Introduction:
Blazor, the innovative web framework from Microsoft, provides developers with two distinct hosting models: Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server. These models offer different approaches to building interactive and dynamic web applications using C# and .NET. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server, helping you make an informed decision based on your project requirements.
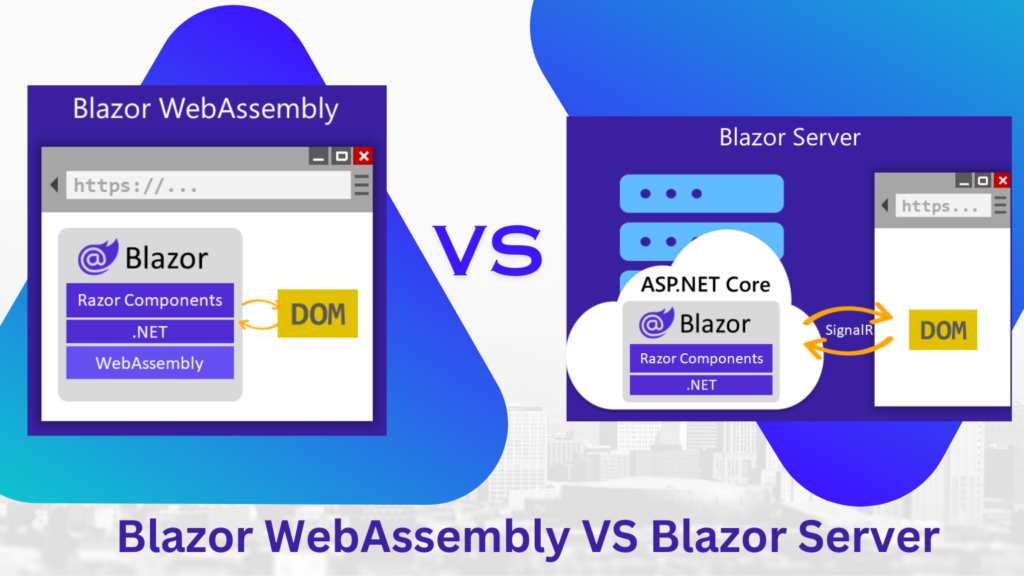
Blazor WebAssembly: Unleashing the Power on the Client Side
Blazor WebAssembly brings the capability to run C# code directly in the browser through WebAssembly. This client-side execution allows developers to create rich and responsive user interfaces without relying heavily on server round-trips. Let’s delve into the advantages and use cases of this hosting model:
Advantages:
- Client-Side Execution: Execute the entire application on the client’s machine, leading to reduced server load and enhanced responsiveness.
- Offline Support: Leverage client-side execution for offline capabilities, ensuring your application functions seamlessly even without a network
connection. - Rich User Experience: Build immersive and interactive interfaces, taking full advantage of client resources and reducing dependence on server
interactions.
Use Cases:
- Applications requiring rich client-side interactions.
- Projects with a need for offline functionality.
- Situations where initial load times are acceptable, and the focus is on enhanced user experience.
Blazor Server: Harnessing Server-Side Power
Blazor Server, in contrast, executes the application logic on the server and leverages SignalR for real-time communication with the client. While the client only receives updates, this model offers advantages in terms of initial load times and server-side processing:
Advantages:
- Reduced Initial Load Time: Minimize the time it takes for users to start interacting with your application by offloading much of the processing to the server.
- Server-Side Logic: Keep the client lightweight by processing logic on the server, particularly beneficial for projects where client-side capabilities need to be streamlined.
- Lower Bandwidth Usage: Transmit only updates and events between the client and server, reducing overall bandwidth requirements
Use Cases:
- Applications prioritizing reduced initial load times.
- Projects with a focus on minimizing bandwidth usage.
- Scenarios where server-side processing is preferred or required.
- Situations where scalability is a key consideration.
Making the Right Choice:
Choosing between Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server involves a careful consideration of your project’s goals and requirements. Factors such as performance, scalability, and the desired user experience should guide your decision-making process. Whether you opt for the client-side prowess of Blazor WebAssembly or the server-side efficiency of Blazor Server, both hosting models offer unique strengths to elevate your web development journey.
In conclusion, Blazor provides a versatile ecosystem catering to various needs. Whether you prefer the client-centric approach of Blazor WebAssembly or the server-side efficiency of Blazor Server, the choice ultimately depends on the specific demands of your project. Embrace the power of C# and .NET in the world of web development, and craft applications that meet the expectations of modern users
